Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy In Adolescents
Obesity has become a global health crisis affecting individuals of all ages, with adolescents increasingly facing the challenges associated with excess weight. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG) has emerged as a viable option for weight loss and metabolic improvement in adolescents with severe obesity. This article aims to delve into the efficacy, safety, and considerations surrounding LSG in adolescents, providing insights into the evolving landscape of bariatric surgery in this population.
Understanding Adolescents and Obesity
Adolescence marks a critical period characterized by rapid physical, emotional, and psychological development. However, it is also a time when obesity prevalence is on the rise, posing significant health risks and impairing quality of life. Factors such as sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary habits, genetic predisposition, and socio-economic influences contribute to the obesity epidemic among adolescents.
The Role of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
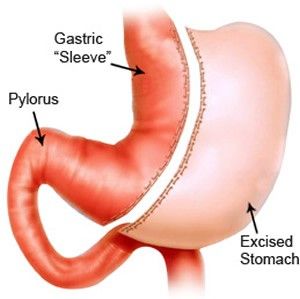
LSG involves the removal of a significant portion of the stomach, creating a smaller, sleeve-shaped stomach pouch. This restrictive procedure reduces stomach capacity, leading to early satiety and decreased food intake. Unlike more complex procedures like gastric bypass, LSG does not involve intestinal rerouting, preserving normal digestive function.
Efficacy of LSG in Adolescents
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of LSG in achieving substantial weight loss and metabolic improvements in adolescents. Weight loss outcomes comparable to those seen in adults have been reported, with significant reductions in body mass index (BMI), resolution of obesity-related comorbidities, and enhanced quality of life. Moreover, LSG has shown sustained benefits over the long term, with many adolescents maintaining weight loss and metabolic improvements years after surgery.
Safety Considerations
While LSG is generally considered safe in adolescents, it is not without risks. Potential complications include surgical site infections, leaks at the staple line, nutritional deficiencies, and gastrointestinal symptoms. Careful patient selection, comprehensive preoperative evaluation, and multidisciplinary management are essential to mitigate risks and optimize outcomes. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and postoperative support are crucial to address any emerging issues and ensure the overall well-being of adolescents undergoing LSG.
Psychosocial Impact
Obesity in adolescence can have profound psychosocial consequences, including low self-esteem, social stigmatization, and increased risk of mental health disorders. LSG has been shown to positively impact psychosocial well-being, with many adolescents experiencing improvements in self-esteem, body image, and social functioning following surgery. However, addressing psychosocial concerns before and after LSG is paramount, as adolescents may require additional support to navigate the emotional challenges associated with weight loss and body transformation.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, LSG in adolescents presents unique challenges and considerations. Skeletal immaturity, hormonal fluctuations, and ongoing growth and development necessitate careful assessment and individualized treatment planning. Long-term follow-up is essential to monitor growth, nutritional status, and metabolic health, ensuring that adolescents continue to thrive beyond surgery. Additionally, addressing lifestyle factors, including diet, physical activity, and behavioral changes, is integral to sustaining weight loss and promoting overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy has emerged as a valuable tool in the management of severe obesity in adolescents, offering significant weight loss and metabolic benefits. While LSG is generally safe and effective in this population, careful patient selection, comprehensive preoperative evaluation, and multidisciplinary management are essential to optimize outcomes and minimize risks. Moving forward, continued research, collaboration, and innovation will further enhance our understanding and approach to LSG in adolescents, ultimately improving the health and well-being of this vulnerable population.