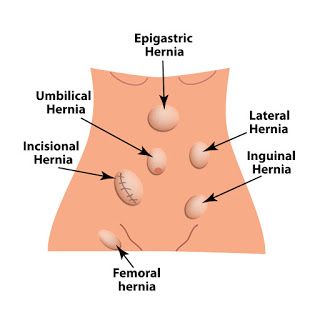
Research And Future Directions In Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic hernia repair has emerged as a transformative approach in the field of surgery, offering patients minimally invasive techniques with reduced postoperative pain and quicker recovery times. As medical science continues to evolve, researchers are delving into new realms to enhance the efficacy and outcomes of laparoscopic hernia repair. In this article, we will explore the current state of research in laparoscopic hernia repair and the promising future directions that hold the potential to reshape the landscape of hernia surgery.
Advancements in Mesh Technology
One of the key areas of research in laparoscopic hernia repair focuses on improving mesh technology. The mesh serves as a critical component in providing support to weakened or damaged tissues, preventing the recurrence of hernias. Researchers are actively investigating novel materials and designs for meshes to enhance their strength, flexibility, and biocompatibility.
Recent studies have explored the use of bioabsorbable meshes that gradually degrade over time, promoting tissue integration and reducing the risk of long-term complications. Additionally, the development of smart meshes equipped with sensors to monitor healing progress is an exciting avenue, offering real-time data to both patients and healthcare providers.
Robotics and Artificial Intelligence
The integration of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) into laparoscopic hernia repair is a burgeoning field with immense potential. Robotic-assisted surgery allows for enhanced precision and dexterity, enabling surgeons to perform intricate procedures with greater accuracy. AI algorithms are being employed to analyze preoperative imaging, assisting surgeons in planning the optimal approach and customizing procedures based on individual patient characteristics.
Telemedicine and Remote Surgery
Advances in telemedicine have the potential to revolutionize the postoperative care and follow-up of laparoscopic hernia repair patients. Remote monitoring devices and virtual consultations can facilitate timely interventions and reduce the need for in-person visits. Moreover, telemedicine can extend its reach to include remote surgical assistance, enabling experienced surgeons to guide and collaborate with their peers in different geographical locations.
3D Printing and Surgical Simulation
The integration of 3D printing technology in surgical planning and simulation has garnered attention in the realm of laparoscopic hernia repair. Surgeons can now create anatomically accurate models of patient-specific hernias, allowing for detailed preoperative visualization and practice. This not only enhances the surgeon’s skills but also contributes to better patient outcomes by minimizing errors during the actual procedure.
Pediatric Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
While laparoscopic hernia repair has been extensively studied in adults, there is a growing emphasis on its application in pediatric populations. Research is underway to determine the safety and efficacy of laparoscopic techniques in children, addressing unique anatomical and physiological considerations. Pediatric-specific mesh designs and instrumentation are being explored to cater to the distinct needs of young patients.
Personalized Medicine Approaches
The era of personalized medicine has extended its influence to laparoscopic hernia repair, aiming to tailor surgical approaches based on individual patient characteristics. Genetic profiling and biomarker analysis are being investigated to identify patients at higher risk of complications or hernia recurrence. This information can guide surgeons in selecting the most appropriate mesh type, suture materials, and surgical techniques for each patient, optimizing outcomes and reducing adverse events.
Global Perspectives on Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Research efforts are not confined to a specific region, as global collaboration brings diverse perspectives and experiences to the forefront. Comparative studies analyzing the outcomes of laparoscopic hernia repair in different healthcare systems and populations contribute valuable insights. Understanding how cultural, economic, and geographic factors influence surgical practices enhances the overall effectiveness and accessibility of laparoscopic hernia repair worldwide.
Environmental Sustainability in Surgical Practices
An emerging trend in medical research, including laparoscopic hernia repair, is a focus on environmental sustainability. Researchers are exploring ways to reduce the environmental impact of surgical procedures, considering factors such as energy consumption, waste generation, and the carbon footprint of medical equipment. Sustainable practices, such as the use of reusable instruments and eco-friendly materials, are being integrated into the evolving landscape of laparoscopic hernia repair.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
As researchers push the boundaries of laparoscopic hernia repair, they also grapple with challenges and ethical considerations. Issues such as patient consent for innovative procedures, equitable access to cutting-edge technologies, and the potential for over-reliance on automation raise important ethical questions. Balancing innovation with patient safety and ethical principles remains a critical aspect of advancing research in laparoscopic hernia repair.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the field of laparoscopic hernia repair is witnessing a dynamic era of research and innovation. Advancements in mesh technology, the integration of robotics and AI, telemedicine, 3D printing, pediatric applications, personalized medicine, global collaboration, and sustainability are shaping the future landscape of hernia surgery. As researchers continue to explore these frontiers, the goal is not only to improve surgical techniques but also to enhance patient outcomes, reduce complications, and make laparoscopic hernia repair more accessible and sustainable on a global scale. With ongoing research and a commitment to ethical practices, the future of laparoscopic hernia repair holds great promise for both surgeons and patients alike.